| HTML | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
| HTML | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Removal of the WHT Flip Ring
| Align |
|---|
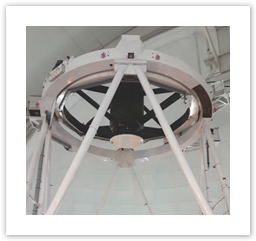
The top end of the 4.2-m William Herschel Telescope (WHT) consists of an outer fixed ring, which is supported by eight Serrurier trusses, and an inner flip ring. The flip ring is attached to the outer ring such that it is allowed to rotate around an axis that allows it to be flipped through 180o. This flipping procedure permits the telescope to be configured with a secondary mirror or with an instrument at prime focus (see Figure 1). |
| Align |
|---|
The WEAVE top-end assembly requires that this inner ring, along with the vanes and the prime focus corrector, is removed; an activity that had never been attempted in the history of the telescope. Prior to removal, an alignment telescope, positioned in the Nasmyth focal station, was used to record the position of the secondary mirror with respect to a reference mark within the alignment telescope (see Figure 2). |
| Align |
|---|
ING astronomers then carried out a Shack-Hartmann analysis to characterise the combined optical quality of the primary and secondary mirrors. The results of this analysis can be seen in Table 1. |
| Align | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 1: The Shack-Hartmann test results, in arcsec, prior to removing the ring. For more information see the WHT optics log. |
| Align |
|---|
The following day, on the 19th of July 2016, ING engineering staff successfully removed the 5.5-tonne flip ring by separating the two bearing housings of the ring from its interface to the outer fixed ring (see Figure 3). |
| Align | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Figure 3: The left-hand bearing, with the dowel pins (only one shown in picture) removed, showed no movement of the bearing housing with respect to the outer ring. After removing the four bolts, a small movement (80µm) to the left of the bearing housing was seen. Before continuing with the process, it was confirmed that this displacement could be recovered. |
| Align |
|---|
The WHT 25-tonne crane, with a series of lifting strops, was used to lift the flip ring (Figure 4). The crane, which is supported from the dome, has a limited patrol range but was proven to be sufficient to allow the rings to be separated. |
| Align |
|---|
Figure 5 shows a series of photographs that were taken at the moment that the two rings were separated. |
| Align |
|---|
Although the task was well-planned, there were a couple of issues that had to be addressed as the activity progressed and these did produce some sweat but thankfully no blood (see Figure 6). |
| Align |
|---|
Once the ring was separated from the fixed ring, it was manoeuvred above GHRIL and lowered to the ground floor (see Figure 7). This was a delicate and slow operation which took about 30 minutes. |
| Align |
|---|
The flip ring was stored overnight in a purpose-built trolley, constructed by SENER and provided by the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) as part of its contribution to the WEAVE project (see Figure 8). |
| Align |
|---|
Figure 9 shows the WHT without the flip ring. In this configuration, the telescope was out of balance by 5.5T but was held in position by a 7-T load which was placed on the ground floor and attached to the blue strops. A secondary restraining system, achieved by securing the fixed ring to the telescope support structure, was also implemented. |
| Align |
|---|
On the 20th of July, the process to replace the flip ring was initiated and four hours later the ring was back on the telescope. The remainder of the day was dedicated to adjusting the ring to its original position, recabling and replacing the items that had to be detached to allow the flip ring to be removed. On the 21st, the telescope was balanced and the test using the alignment telescope was repeated (see Figure 10). This test showed no discernible differences when compared with the results of the test that was carried out prior to removing the ring. |
| Align |
|---|
During the night of the 21st, the astronomers repeated the Shack-Hartmann analysis and concluded that there was no significant change in the optical quality of the telescope (see Table 2). Interestingly, there was a reduction in the amount of coma observed. |
| Align | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Table 2: The Shack-Hartmann test results, in arcsec, after the ring was replaced. For more information see the WHT optics log. |
| Align |
|---|
The telescope is now fully operational and a plan of additional work is being proposed to simplify the removal process. This marks a significant milestone in ING's preparations to receive WEAVE. The current expectation is that this procedure will need to be carried out once per semester with the removal taking less than seven hours to complete. |
| Borderless table | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|